Image Pre-Processing in Machine Vision Systems
Optimize image data and streamline vision systems
Image pre-processing is a central component of modern image processing systems. It is used to optimally prepare raw image data from machine vision cameras for the subsequent processing steps. The aim is to optimize image information, clean up image data and, if necessary, efficiently reduce the amount of data. Users benefit from higher image quality and reduced load on the host PC, which in turn can reduce system costs.
Last updated: 01/12/2026
What is image pre-processing?
Image pre-processing refers to all steps that influence the image data before the actual image analysis. Specialized algorithms and technical processes are used directly on the machine vision camera, in the frame grabber, or in the embedded system. Image pre-processing optimizes the data for specific application requirements, increases image quality, and reduces the load on the host PC. It is essential for precise, fast, and robust image processing solutions.
Image pre-processing can be divided into two categories: image data cleansing without reducing the amount of data and image data reduction.
Image data cleansing: Optimization without data reduction
Image data cleansing refers to all pre-processing steps that improve the quality of the image data without significantly changing the image information or size. The aim is to provide unadulterated and optimally usable raw data for subsequent image processing.

Typical methods of image data cleansing include
Debayering: Reconstructing color information from the sensor signals of a color filter array
White balance: Correctly color adjusting the image for different light sources or lighting conditions
Noise reduction: Reducing image noise using suitable filter or model methods
Image sharpening: Increase the perceived sharpness of detail and edges in the image
Shading Correction and Flat Field Correction: Compensating for brightness and/or color deviations across the entire image field
Dead pixel correction: detecting and replacing faulty sensor elements by interpolation of neighboring pixels
Geometric rectification: Correcting optical distortions (e.g. barrel or pincushion-shaped), often by means of geometric transformations such as affine or projective mappings
These steps ensure that relevant structures stand out more clearly and reproducible results are achieved - without losing relevant image information.
Data reduction through image pre-processing
In contrast to image data cleansing, data reduction aims to reduce the volume of data in a targeted manner, for example by concentrating on image content that is relevant for further processing. This provides savings in the purchase of cost-intensive computing units such as CPUs and GPUs, or increases the processing speed and optimizes the use of available resources.
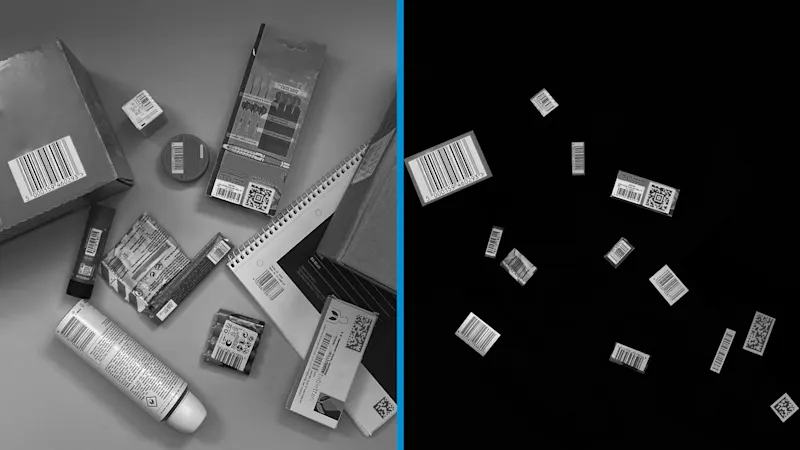

Methods of data-reducing image preprocessing are:
Region of Interest (ROI) selection: Automatically or manually select relevant image areas to process or transfer only the required image data
JPEG compression: Reduces the data volume through lossy image compression with controllable loss of quality
Bit rate reduction: Reduces the quantized greyscale or colour resolution (e.g. from 12 bits to 8 bits) to reduce the data rate
Histogram stretching or flattening: Contrast adjustment by redistributing the gray values to make better use of the available dynamic range; can increase information density, but does not reduce the amount of data per se
Filtering of unnecessary content: Suppresses or removes unnecessary image areas or image components (e.g. background, noise, or unimportant frequencies) before storage or transmission
JPEG compression: No CPU load for compression. Intelligent pre-processing helps to reduce JPEG artifacts - without reducing bandwidth.
By using such methods, the data throughput can be significantly increased, transmission bottlenecks avoided, and the performance of the application improved. This is particularly important for high-speed applications or in embedded vision systems with limited resources.
Application examples for image pre-processing
Image pre-processing is a key factor for efficiency and accuracy in a wide range of industrial image processing applications. With the targeted use of different methods, machine vision systems become more efficient, faster, and more robust.
PCB inspection in electronics production
In PCB inspection, image data is cleaned up to reliably visualize defects such as solder joint errors or short circuits. Noise suppression and image sharpening enhance relevant structures; subsequent contrast enhancement ensures clear differentiation of defective components. Targeted ROI selection means that only critical sections are transmitted and evaluated. This minimizes the transmitted data and increases the inspection speed at the same time.

Object tracking and classification in logistics
For automatic object detection and tracking in logistics centers, image pre-processing is already used in the camera. Image data is denoised in advance, geometrically rectified and, if necessary, color space converted. Segmentation and blob analysis on the frame grabber can be used to select and characterize parcels or containers, for example. Data reduction by transferring selected object areas increases speed and makes classification more precise.
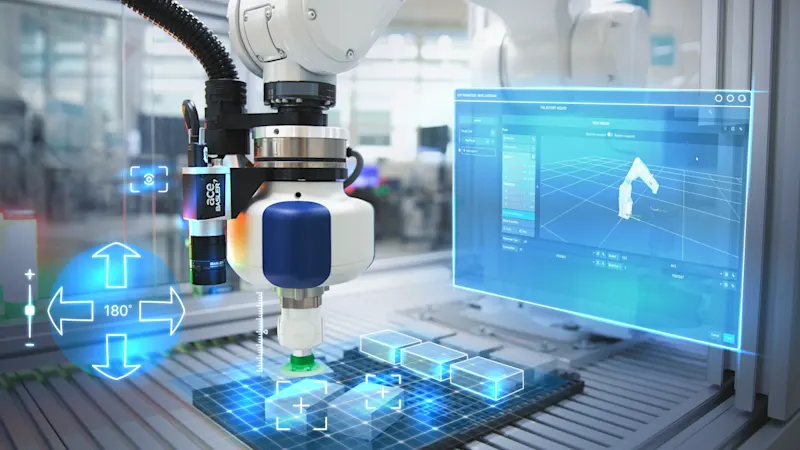

Object recognition in robotics (pick & place)
In pick & place applications, debayering and white balancing can improve the basic quality of the camera image. ROI selection reduces the volume of data to be processed by reading out only the relevant image areas. Geometric rectification can compensate for perspective distortions caused by an angled camera arrangement. This provides the robot system with optimized image data, which noticeably increases the recognition accuracy for the position and gripping point of the object.
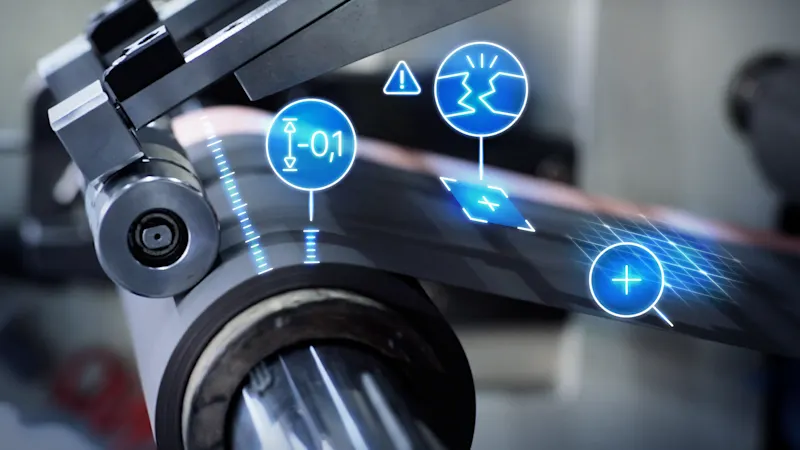

Quality assurance in battery cell production
The high production speeds in the electrode coating of substrate films generate large amounts of data. By determining the ROI in a frame grabber, initially only the areas with irregularities are localized. Only the image data of the ROI is then viewed and further processed. This means that the CPU of the IPC can continue to be used for the actual system control without any additional load.

Image pre-processing on Basler cameras
Pre-processing in the camera reduces the amount of data to be transmitted by compressing image data. This is particularly important when interfaces can only transfer limited amounts of data or the system has little computing power.
Basler cameras already offer a basic level of pre-processing such as debayering, color anti-aliasing, image sharpening, and noise reduction. These processes can significantly improve the brilliance, detail, and sharpness of the image and also reduce noise.

Image preprocessing on the frame grabber
The image data is transferred from the camera to the frame grabber where it is pre-processed. Frame grabbers are particularly necessary for real-time requirementsand large amounts of data. They enable extensive pre-processing directly on the FPGA.
This makes a vision system with a frame grabber the ideal solution for fast frame rates and high resolutions.
Standard frame grabbers offer functions such as debayering, look-up tables, and mirroring. However, programmable frame grabbers allow even more.
Image pre-processing on programmable frame grabbers
Use programmable frame grabbers if image data needs to be processed quickly and/or in a complex way before it is sent to the PC. They are particularly useful when standard frame grabbers are not sufficient in terms of speed, interface, or pre-processing requirements.
VisualApplets - Image preprocessing in real-time applications on FPGA processors
Our FPGA experts use VisualApplets to develop powerful image pre-processing for you. Features such as RAW-to-JPEG compression, blob analysis, and other operators for image optimization increase the speed and robustness of vision systems.
Image data cleansing
Pixel errors, geometric distortions, exposure scattering, or colour inaccuracies can be reliably minimized with the help of a variety of powerful operators.
Data reduction
With intelligent processes such as blob analysis, efficient RAW-to-JPEG compression, or the transfer of pre-processing functions directly to the camera's FPGA, the data volume can be reduced at the source.
Do you have special requirements for your application that you would like to discuss with us? We are happy to help you.
Current trends: Artificial intelligence (AI) makes image pre-processing even more efficient
With the help of AI-based algorithms, we can now integrate complex image pre-processing steps (such as adaptive noise reduction, automatic defect detection, or intelligent segmentation) directly into the camera or edge hardware. Deep learning models make it possible to adapt pre-processing to specific applications much more precisely - for example, by using adaptive filters that adjust independently to changing conditions in the production environment. At the same time, it is possible to interlink pre-processing and analytical evaluation more closely: AI can not only clean or optimize image data, but also identify initial characteristics and conspicuous features, which significantly increases the efficiency of subsequent process steps. Modern machine vision systems are increasingly relying on the combination of classic algorithms and AI to provide robust, flexible, and future-proof solutions for demanding applications.
Our products and solutions for image pre-processing
Image pre-processing is the key to precise and efficient vision systems. It improves image quality, accelerates analysis processes, and ensures a lean workflow.
Frequently asked questions about preprocessing
Image pre-processing comprises all steps that optimize raw image data from machine vision cameras before the actual image evaluation. The aim is to increase image quality, clean up image data, and efficiently reduce the volume of data.
Image pre-processing highlights relevant image information, improves image quality, and relieves the system of unnecessary computing loads. This enables more precise and faster evaluations while increasing the reliability of automation solutions.
Image pre-processing can take place directly on the machine vision camera, in the frame grabber, or in the embedded system. The specific architecture depends on the performance requirements and application environment.
Image pre-processing can be divided into two areas:
Image data cleansing:
Increases image quality without losing information or image size.
Data reduction:
Reduces the data volume in order to speed up transmission and processing.
Typical methods of image data cleansing are
Debayering (color reconstruction)
White balance (color fidelity in fluctuating light)
Noise suppression (filter against interference signals)
Image sharpening (emphasizes details)
Shading correction/flat field correction (compensates brightness/color)
Dead pixel correction (corrects defective sensor pixels)
Geometric rectification (corrects optical distortions)
Data reduction in image pre-processing is performed by:
ROI selection (only read out relevant image sections)
JPEG compression (reduces file size through compression)
Bit rate reduction (reducing the image depth)
Histogram stretching/flattening (optimizes contrast)
Filtering of irrelevant content (removes unnecessary image areas before transmission)
The advantages of image pre-processing include:
Improved image quality (sharpness, less noise)
Relieving the host PC through upstream algorithms
Cost-efficient system architecture thanks to data reduction
Increased speed and reliability of the overall system
A suitable choice of hardware and software, modular interfaces, as well as simple maintenance and parameterization are important. The selected methods must deliver reproducible, application-oriented results.