Image Quality for Camera Systems
What makes a good picture? The answer goes beyond just sharpness and contrast. When selecting a camera for your vision system, it's important to consider additional key factors like sensor size, pixel count, image noise, exposure, and exposure time. External conditions also influence image quality, as vision systems often have unique requirements. We break down the essential criteria to help you compare cameras effectively.
How do you assess image quality?
What criteria are important for assessing the image quality of a camera? How can you determine the camera that will deliver the optimal image quality based on these criteria?
In our white paper, we answer the following questions:
How do you assess the image quality of different cameras?
How do you create comparable conditions for a camera assessment?
Can the digital gain be used to improve image quality?
What influence do factors such as sensor and pixel size, amount of light, dynamics, SNR, and resolution have on image quality?
Making camera criteria comparable
In camera technology and machine vision, many factors influence image quality and the choice of an optimal vision system. To simplify the comparison of industrial cameras, the European Machine Vision Association (EMVA) introduced the EMVA1288 standard. This standard allows for straightforward comparisons across camera technologies using key metrics like pixel characteristics, saturation capacity, and sensor type.
For a meaningful camera comparison, it’s essential to use an identical sensor. Key parameters, including lighting, exposure time, object distance, and lens type, should also be consistent to accurately assess image quality. The data in the EMVA Data Sheet were obtained under these controlled conditions, allowing for a clear, reliable comparison.
Image quality: decisive criteria for buying your camera
Whether it’s an industrial camera or consumer camera, the factors that determine excellent image quality are similar. When choosing a camera—whether a system camera or an SLR—consider the following criteria to answer the question: What defines image quality?
Pixel count and sensor size: affect detail accuracy and performance in different lighting conditions.
Quantum efficiency (QE): determines how well the sensor converts light into an electrical signal, especially in low light conditions.
Image noise and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR): a good SNR ensures noise-free images, especially at higher ISO values.
Dynamic range: measures the ability to capture detail in light and dark areas, which improves color reproduction.
Brightness and illumination: performance in different lighting conditions is crucial for image quality.
Sharpness: depends on the quality of the lens and image processing, and affects the overall quality of your photographs.
Contrast: high contrast makes for more vivid and impressive shots.
Following these criteria will help you select a camera that provides optimal image quality
Important factors for image quality
Sensor size and pixel count
Sensor size and pixel count are essential for achieving high image quality, as the sensor converts incoming photons into electrons, which are then processed to create image information. Pixels on the sensor enable this conversion.
Different sensors have varying quantum efficiencies, which means they convert photons into electrons at different rates. Higher quantum efficiency results in more image information, contributing to better image quality.
Additionally, the number and size of the pixels impact image quality. Too many small pixels can lead to increased image noise, meaning even a large sensor that captures a lot of light won’t automatically produce high-quality images. Achieving optimal image quality requires a balanced combination of sensor size, pixel count, and pixel size.

Image noise and SNR
Image noise is an unwanted visual disturbance that appears as a grainy effect in most digital images. It is caused by several factors, including variations in the light reaching the sensor and electronic noise within the camera’s circuitry.
A high-quality camera aims to minimize image noise and separate it from the image signal. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) describes how well this succeeds. A higher SNR means that the signal is less affected by noise, resulting in better image quality.
When selecting a camera, factors like sensor size, pixel count, exposure, and contrast are critical to image quality. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) should also be considered to fully answer the question: What defines image quality?
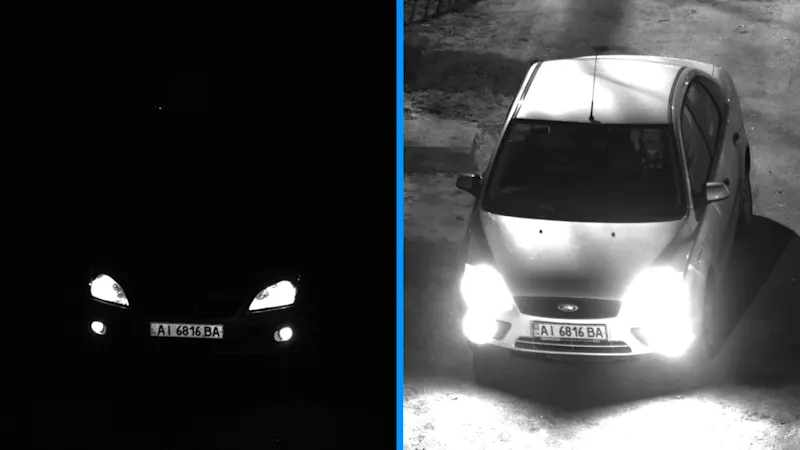

Dynamic range in cameras
Dynamic range significantly influences a camera's image quality, defining how well both bright and dark areas of an image are captured. Pixels are essential to this process: in bright areas, they absorb many photons, while in dark areas, they require less light. Insufficient exposure time can compromise image quality, causing dark areas to appear blurry and bright areas to become overexposed.
A camera with a good dynamic range should ideally have a large sensor with large pixels to capture ample light and maintain balanced detail. This is especially crucial in high-contrast scenes, such as in traffic and transportation, where both bright license plates and darker elements, like drivers, need to be clearly visible.
The entire vision system at a glance
In this article, we have highlighted numerous technical aspects, but in the end, image quality depends on the overall vision system:
What purpose do you want your camera to serve?
What is the ambient light like in your vision system?
Which camera criteria are most crucial for your application?
At Basler, our years of expertise support you in making informed decisions when selecting and comparing camera systems. With our extensive product portfolio, we offer the ideal vision system for your application.
Our products for optimal image quality
Basler cameras deliver exceptional image quality. Paired with the right lenses and lighting, they create an optimal vision system tailored to your application.


