Color Calibration of Industrial Cameras
Optimized color accuracy for precise image processing
Color information plays a critical role in many industrial applications, especially in the medical field. In areas such as pathology, ophthalmology, and dermatology, accurate and standardized color reproduction is essential for reliable diagnosis. We explain how cameras can be calibrated for maximum color fidelity in just seconds, even without a predefined light source setting.
Color calibration for Basler cameras
In our white paper, we explain why the calibration of Basler color cameras is important and outline the key steps involved
What is meant by color and what color systems are there?
What are the advantages of the RGB color space?
What benefits does a calibrated camera offer?
What are the four steps of color calibration at Basler?
Why color calibration is crucial
Color information plays a central role in many image processing applications - from color inspection in the packaging industry to diagnostic support in medical imaging. A beautiful image display is not enough: What matters is precise, measurable, and repeatable color reproduction.
Standardization for high accuracy
In practice, images are often taken in different rooms, with different lighting conditions, camera models and at different times . To ensure that such images can be reliably compared with each other - for example in the case of progress observations or serial measurements - the color rendering must be standardized.
The process that creates this standardization is color calibration. This is the only way to ensure that the colors of the camera images on the monitor match the colors of the real object - for example in daylight. In many applications, this high color fidelity is the prerequisite for meaningful diagnoses or precise automated decisions in industrial production.
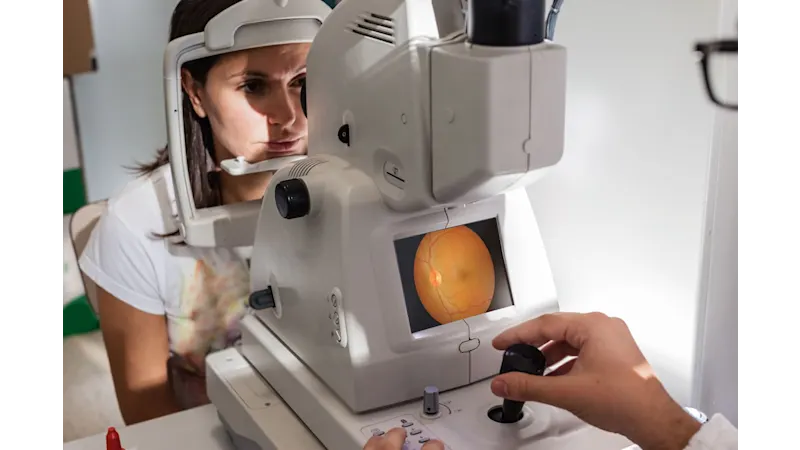
Medical application: Color in ophthalmology
An illustrative example is provided by ophthalmology:
When examining the retina with fundus cameras, the interpretation of the image data depends directly on the correct color representation. The doctor can see from the camera image whether the vessels in the retina are intact or show abnormalities - such as changes in the color of the tissue due to a lack of oxygen.
Only a color-calibrated camera can reliably image such changes and thus contribute to the early detection of diseases such as macular degeneration.
How does color calibration work?
Color calibration optimizes the camera's color calculation pipeline - i.e. all internal calculation processes that lead from the sensor signal to the finished image.
The calibration process at a glance:
Reference image with a color chart
A standardized colour chart (e.g. ColorChecker) is recorded under real lighting conditions.Comparison with reference values
The target values are known for each color field (usually in the sRGB color space). The color value of the camera is compared with the target color value.Calculation of the color error (ΔE)
The difference is specified as color error ΔE - the lower the value, the better the camera reproduction matches reality.Adjusting the camera parameters
White balance, color matrix, gamma curve and other parameters are adjusted so that the ΔE is minimized across all colors.
After calibration, additional color adjustments can be made, for example to comply with special color profiles.
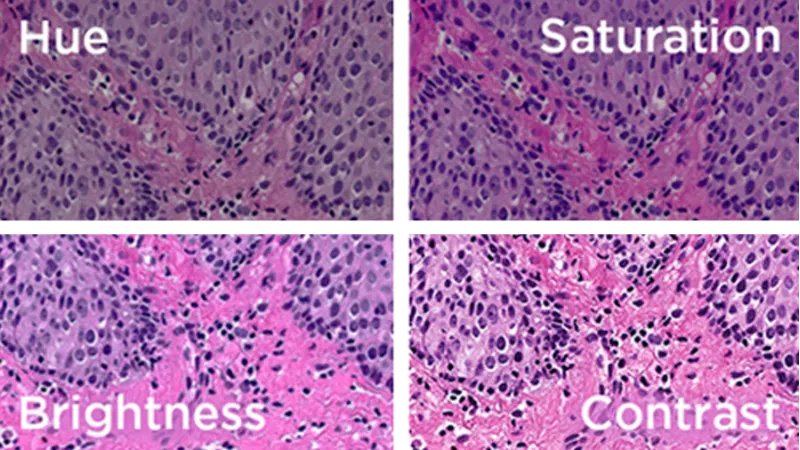
Useful functions for color-accurate image processing
Modern industrial cameras offer a range of integrated functions that are essential for accurate color processing:
Color presets (e.g. daylight, LED, artificial light)
Adjustable parameters for hue, saturation, brightness and contrast
Six-axis color control for targeted adjustment of individual colors
Automatic or manual white balance
Especially for medical applications or high-precision industrial processes, the use of presets is not sufficient. Calibration is always carried out under real lighting conditions - to ensure reliable color reproduction in the subsequent application.
Application example: calibrating the Basler MED ace camera
With the Basler MED ace camera, color calibration is performed by software. If no suitable light source preset is available, your industrial camera can be calibrated in just a few seconds using the Basler Color Calibrator software.
How color calibration works
The first step is to align the camera with the color card so that the card is fully visible in the image.
The software then adjusts the brightness to the optimum values.
In the next step, the software performs complex calculations such as white balance and color matrix optimization.
Finally, the six-axis operator is set to the best possible color values.
The result is the ideal light source preset for the current lighting conditions. If you are satisfied with the results of the recalibration, the color settings can be saved in the cameraor be exported to other cameras.
Conclusion: calibrated color accuracy for precise medical imaging
Trust and accuracy are crucial in medical imaging. Doctors and healthcare professionals rely on high-quality, color-accurate images for examinations, diagnosis, and aftercare. Calibrated imaging devices help ensure consistent color reproduction and standardized colors across different systems and lighting conditions, delivering reliable results over time.
Intelligent and user-friendly cameras enable fast and accurate color calibration in seconds. These advanced solutions will further improve the reliability and efficiency of Medical & Life Sciences.
Our products for image processing in medicine
Benefit from the specially designed Basler MED ace camera series along with our experience in developing individual machine vision solutions for your requirements.
