Achieve Perfect Image Uniformity With Shading and Flat Field Correction (FFC)
High-speed, industrial automation lines use multiple sources of illumination and cameras. This setup often leads to varying background uniformity in captured images. Flat Field Correction (FFC) and Shading Correction are commonly used algorithms in the machine vision market to achieve image uniformity and quality.
Challenges in the image quality of high-resolution vision systems
In high-resolution imaging for semiconductor manufacturing or other high-precision AOI inspections, high-speed industrial automation lines utilize multiple illuminations and cameras, which can be triggered simultaneously or separately to detect minute defects. However, this setup often leads to varying background uniformity in captured images, which is undesirable as it does not originate from the object of interest. Image artifacts like lens vignetting, camera sensor imperfections, surface texture irregularities, and uneven illumination contribute to inaccurate feature detection, measurement errors, and compromised quality control.
Different correction algorithms address different artifacts
To address issues with the image quality, various correction algorithms are used. Some algorithms specifically target sensor-related fixed pattern noise (FPN), which includes two primary components: dark signal non-uniformity (DSNU) and photon response non-uniformity (PRNU). Other algorithms address non-sensor-related issues, such as shading or vignetting. Flat Field Correction (FFC) and Shading Correction are commonly used in the machine vision market to achieve image uniformity and enhance overall image quality.
The different versions of the Flat Field Correction algorithm
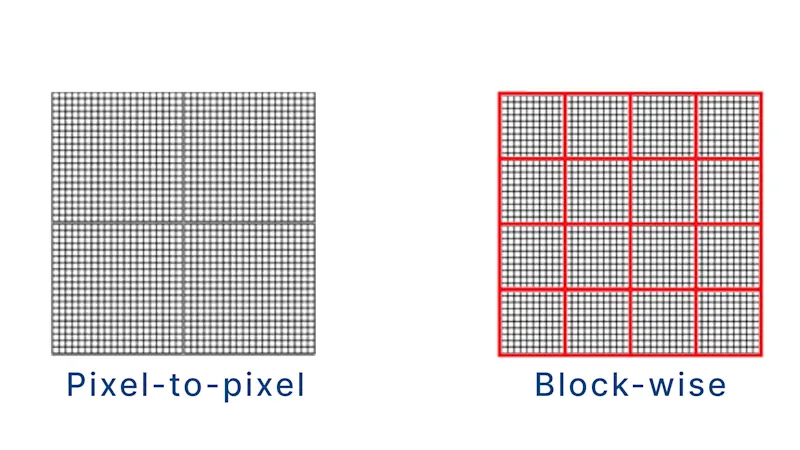
However, Flat Field Correction (FFC) is interpreted and used differently by various machine vision suppliers, leading to varying result quality. More importantly, different applications usually have their individual requirements, and one-size-fits-all solution usually doesn’t work.
Pixel-to-pixel correction is ideal for sensor-related artifacts but requires extensive storage capacity. Conversely, for optical or illumination-related issues, block-wise correction—where small square segments of adjacent pixels are treated as a unit—is more efficient.
Low-resolution sensors benefit from simpler, cost-effective FFC solution in common vision tasks. However, high-bandwidth, low-latency imaging applications face limitations with fixed algorithms due to storage constraints and inflexibility in camera settings.
Custom Flat Field Correction
When the fixed correction algorithms in-camera or on frame grabbers are insufficient, Basler offers advanced and flexible solutions through FPGA programming with VisualApplets software for perfectly uniform images. Beyond our existing FFC algorithms, you have the flexibility to modify the details of the feature with our additional services and support, ensuring precise FFC interpretation for your specific applications.
Examples of the additional options include:
Multiple sets for different illumination sequences, exposure times, and gain levels
Adaptive modes with temperature calibration
Noise reduction
Automatic defect pixel detection/correction by local adaptive thresholding
Sequence-related options
Your benefits
Advanced, customizable FFC and shading correction tailored to specific applications, surpassing standard camera solutions.
Complete flexibility to customize and adjust features according to your requirements
Dedicated support from the experienced Basler team, specializing in these advanced approaches for over 15 years
No runtime license cost
Products for this solution
Looking to implement a comparable solution? These products will help you.