Embedded Vision Solutions as Smart Sensors for IoT Applications
Our live demo shows how an embedded vision solution can be used as an efficient and intelligent sensor for image data classification. Read more about it.
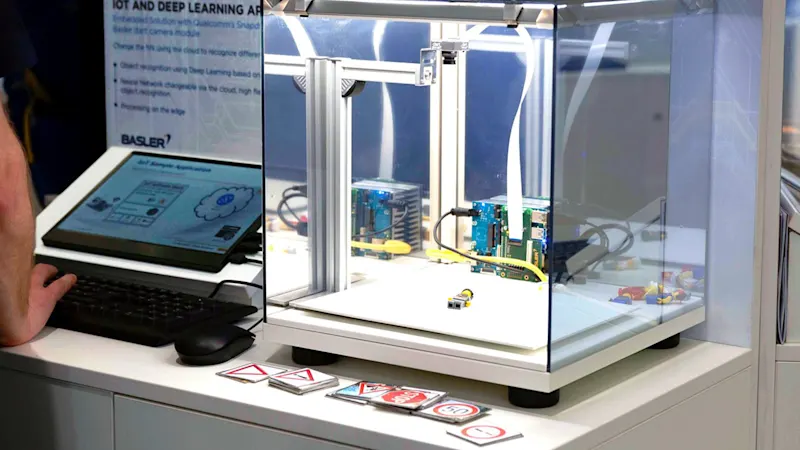
How the smart IoT applications work
IoT sensors, such as a camera, are usually only connected to the cloud with very low bandwidth. Therefore the transmission of the large amount of image data would be slow. One solution approach is to perform the analysis of the image data at the location of the camera sensor itself, "on the edge" (Processing on the Edge), and then only transfer the evaluated data to the cloud. A connection with a very low bandwidth is completely sufficient for this purpose. Accordingly, the transfer to the cloud can be carried out very quickly and the camera can react to an incident.
Step 1: Find the right hardware for the embedded vision system
This live demo is based on the award-winning Basler Embedded Vision Kit. This kit consists of
a dart BCON for MIPI camera module by Basler
a 96 Boards™ compatible processing board with Qualcomm® Snapdragon™ SoC and
a 96 Boards™ compatible mezzanine board to directly connect the camera module to the processing board
This solution allows image data captured by the camera module at high frame rates to be processed directly on the processing board.
Discover the Embedded Vision PortfolioStep 2: Train neural networks for classification
The aim of the live demo is to be able to classify different Lego figures (craftsman, astronaut, cook etc.) or different traffic signs. This task is performed by neural networks, more precisely by Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs).
Basler initially trained two different CNNs, one for the classification of Lego figures, the other for the classification of traffic signs. The trained CNNs are not very large with only a few megabytes and can be transferred from the cloud to the edge device in an acceptable amount of time via a low-bandwidth connection. After transferring the Lego figure CNN, the Edge Device was able to reliably classify the figures and report the result to the cloud with low bandwidth requirements and low latency. To "retool" the Edge Device to classify traffic signs, only the corresponding traffic sign CNN had to be transmitted from the cloud, so that the smart sensor was then able to reliably detect different traffic signs.
To the software for embedded visionThe advantages of the embedded vision solution at a glance
low bandwidth requirements for linking the sensor to the cloud
low latency in the reaction of a cloud application to a sensor event
ideal opportunity for simultaneous “remote maintenance” of multiple sensors OTA (sensor configuration, firmware update or e.g. uploading a new CNN for a new classification task)