What Is Time-of-Flight?
Time-of-flight (ToF) technology enables the precise capture of 3D images based on the time that it takes for light to reach and then be reflected off of an object, or the degree of phase shift in the reflected light. Combining 2D image data and 3D depth information opens up efficient solutions for factory automation, robotics, logistics, medicine, and autonomous vehicles. We explain how a ToF camera works, the advantages and potential limitations of ToF, and show typical application examples.

Stronger 3D performance with Time-of-Flight technology

Time-of-flight cameras are ideal for real-time applications that require precise measurements at a long working distance. Watch our webinar to learn how compact ToF cameras simplify application complexity and reduce overall system costs.
Watch the 3D webinarThe camera at the heart of time-of-flight technology
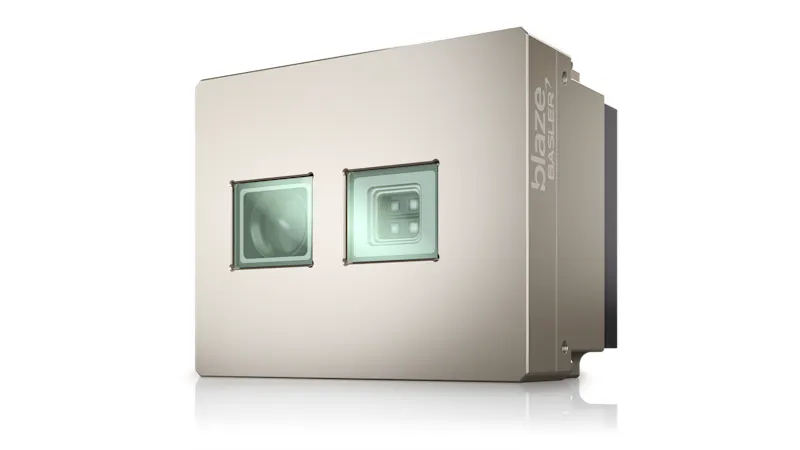
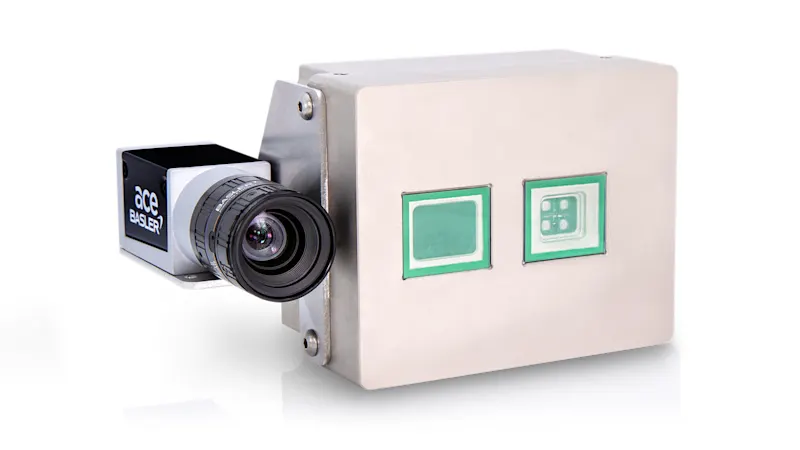
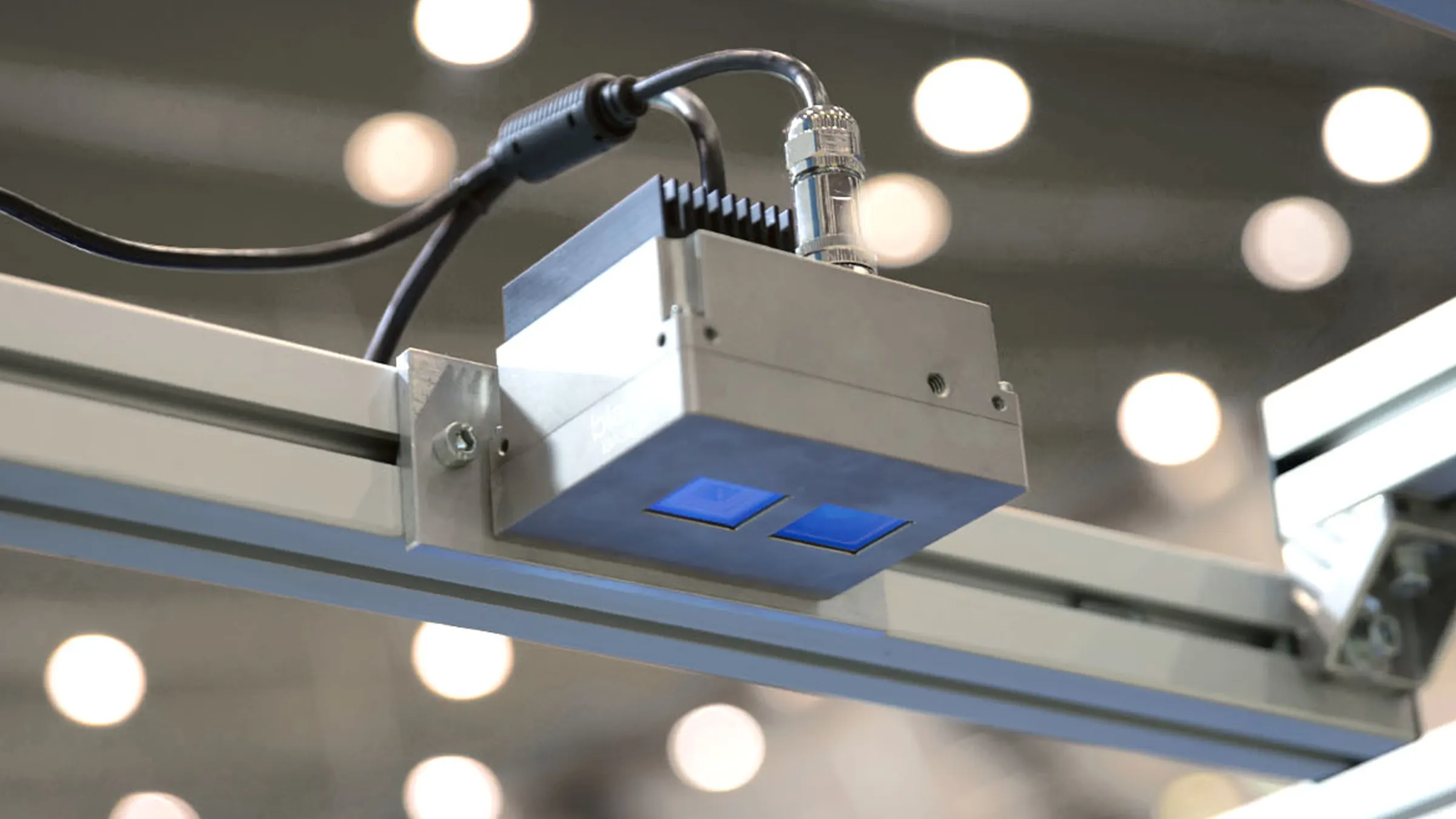
A ToF camera consists of an integrated light source, a lens optimized for ToF, a sensor that stores the captured image data, and an interface for communication with external devices. The camera emits either continuous or pulsed light waves and measures the time or phase shift of the reflected light to calculate the distance of objects in the scene and create a detailed depth map in which each pixel represents distance information.
This feature is crucial because it bypasses the need for complex algorithms to determine depth, which is a challenge for conventional imaging systems such as stereo vision systems. ToF cameras are characterized by their compact design, ease of use, accuracy and high frame rates. This makes them attractive for cost-effective 3D imaging solutions. In addition, ToF technology delivers reliable results even in difficult lighting conditions, which extends its range of applications.
Pulsed or continuous light
Regardless of which principle you use, you can use a light source that can illuminate the entire scene to determine the depth of all points in the scene with one shot. The result is a distance map in which each pixel encodes the distance to the corresponding point in the scene.
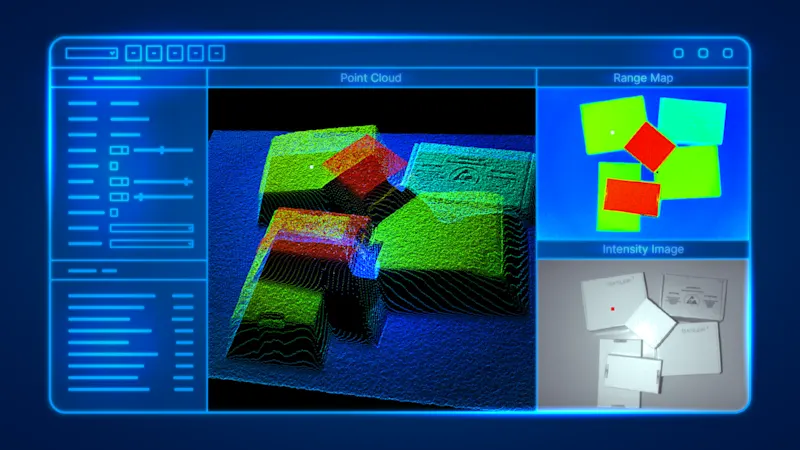
What does a ToF image look like?
This example shows the depth information as a pseudo color image. Blue means far away, red is close.
As the ToF camera records a normal 2D intensity image in parallel to the depth information, both pieces of information can be merged to create a textured 3D graphic.
Time-of-flight applications are revolutionizing the industry
Logistics and packaging
In the fast-paced world of logistics, ToF technology provides precise support for packing, from filling boxes to stacking and scanning volume. Accurate depth information helps to efficiently place labels and monitor loading and unloading operations, ensuring optimal use of space and resources in warehouses and during transportation.
Robotics and factory automation
Factory automation and robotic applications benefit greatly from time-of-flight cameras. They help automate complex tasks such as object recognition, picking, assembly, and quality control, e.g. detecting damaged parts or errors during stacking. The 3D data from ToF cameras enables robots to interact more intelligently and autonomously with their environment.
Patient care in medicine
ToF technology has also found an important role in the healthcare sector. Camera systems based on this technology enable non-invasive patient monitoring and accurate patient positioning during surgery, ensuring both patient safety and improved clinical outcomes.
Autonomous vehicles
ToF technology in autonomous vehicle systems contributes significantly to navigation accuracy and safety by providing real-time 3D data that can be used by autonomous driving systems to detect obstacles, estimate distances and issue necessary warnings or corrective actions.
Into the 3D future with time-of-flight
Factors such as stray light due to unwanted reflections, multipath effects due to multiple light reflections, saturation by ambient light, and interference from other active vision systems must be taken into account. Nevertheless, the advantages of integrating ToF technology outweigh these limitations in most scenarios.
As the technology continues to evolve and overcome these obstacles, time-of-flight technology remains a robust, fast and cost-effective approach to 3D imaging. As the industry realizes its potential, ToF will become a cornerstone of machine vision and open up the entire spectrum of 3D imaging applications.
By seamlessly capturing the third dimension, ToF cameras are becoming indispensable tools in various sectors - paving the way to a future where depth perception is an essential part of automation and machine intelligence. Whether it's streamlining logistics, supporting robotics, improving patient care, or paving the way for the autonomous vehicles of tomorrow, ToF technology is revolutionizing the machine vision industry by providing 3D information.
Our time-of-flight products
Deepen your knowledge of time-of-flight with our webinars and white papers
3D technologies such as stereovision, structured light, laser triangulation and time-of-flight influence many areas of Industry 4.0 and enable advantages in a variety of applications. Our webinars and white papers compare the processes and performance of the various technologies.