Microwave Imaging
Automated, damage-free screening of packaging
From the early detection of faulty parcels to the optimization of storage locations: In logistics, millimeter wave technology opens up new possibilities in quality assurance and inventory management. With this innovative technology, we offer precise detection of content, structures, and potential anomalies in real time.
Non-destructive screening
Microwave imaging inspects packaging from the outside - it is completely contactless, without opening or damaging materialsReliable under real logistics conditions
Resistant to environmental influences: Functional in dust, smoke, fog, rain, or hailInnovative & safe vision technology
New, scalable vision technology with many application areas, safe and harmless for humansDetection of overlapping and concealed objects
For error-free packaging inspection - even with complex, multi-layered or confusing contents
How does microwave imaging work?
A technology that can see through fog, fabrics, and even walls: Microwave Imaging uses microwave radiation. This produces non-invasive and safe images that provide deeper insights into internal structures. The system's camera converts the signals received from the microwave sensor into digital images. This provides the user with clear representation of the internal structures of objects.
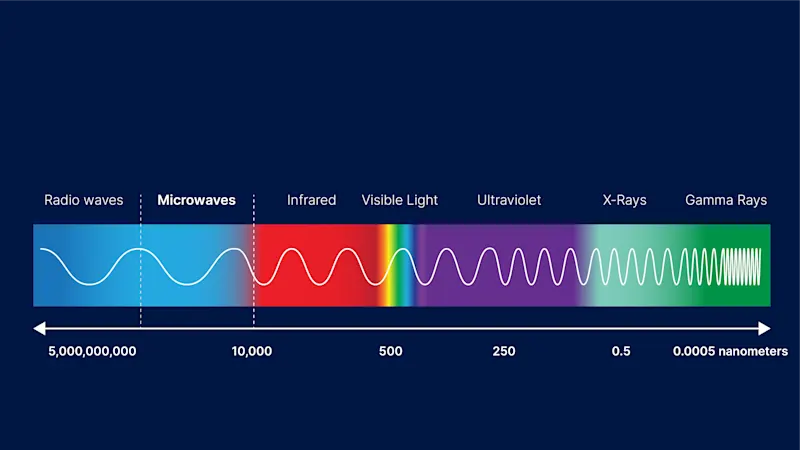
Millimeter waves for scanning objects
Unlike conventional cameras, microwave imaging technology works by emitting and receiving millimeter waves. The length of these millimeter waves lies between that of light and that of radio waves. They therefore have a combination of the properties of these two waves: They are invisible to the human eye, but propagate like light in a straight line in all directions. This allows us to look insidepackaging to detect hidden objects or anomalies - safely and non-destructively.
Short-wave infrared light (SWIR) is absorbed or reflected by many materials, but when microwaves are used, many objects are penetrated more deeply: Plastic, wood, cardboard, and fabrics are transparent to these waves, so structures behind them become visible. Metals are the only reflective material.
Compared to X-rays , microwave imaging is harmless and can be used without a permit. This makes it particularly well suited for use in industries where speed and safety are crucial.
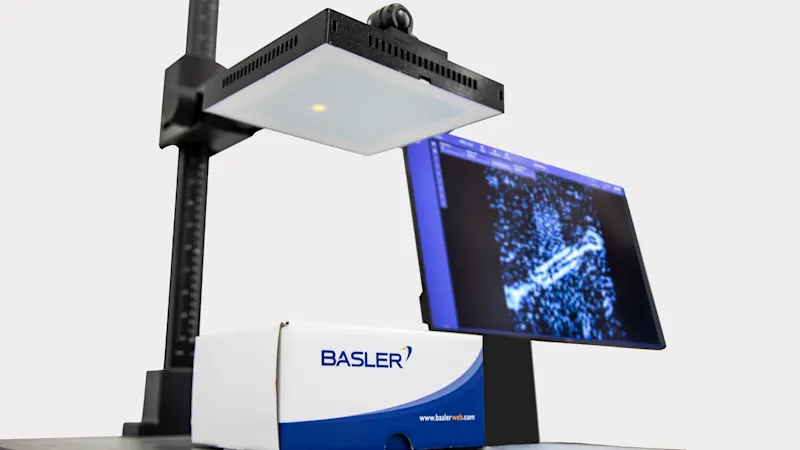

The system set-up
With millimeter wave technology, an object is illuminated by a mm-wave transmitter. The reflected rays are then recorded by the camera using a sensor array: This is a combination of different sensors in one module, which take certain measurements simultaneously.
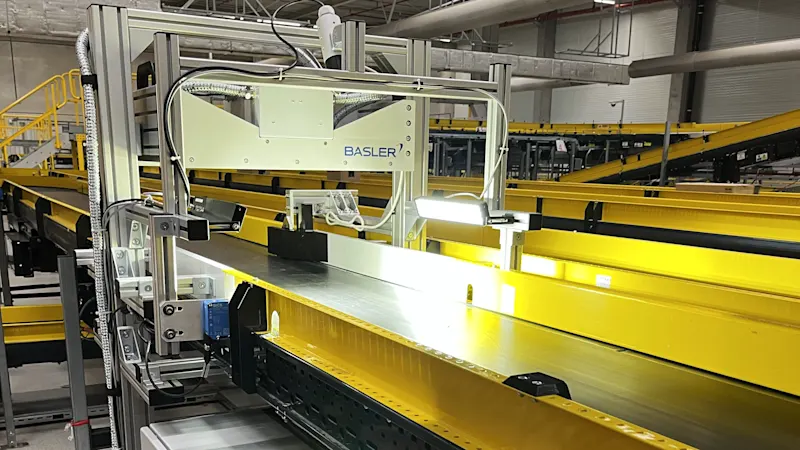

Non-destructive screening of packaging
Our microwave imaging system creates clear, unambiguous images of the inside of packaged products - without opening or damaging the material. Ideal for automated inspection processes in logistics.
Harmless and healthy electromagnetic waves for people and the environment
Insensitive to difficult environmental conditions such as dust, smoke, rain, fog, hail, bright sunlight, and extreme temperatures
Typical application areas for millimeter waves in logistics
Millimeter wave technology is used in logistics to improve the efficiency and security of supply chains. It enables the detection of objects and the identification of damage. Contents can be checked in parcels without opening them - which contributes to theft prevention and process optimization.
What does innovation project mean?
We are currently looking for partner companies with whom we can jointly validate use cases and implement initial pilot projects. If you have a suitable use case, please contact us.
As a project in the innovation phase, we are concentrating on using our customers' experiences to see how well mm-wave imaging can be used in real applications and which use cases are generally possible
To do this, we want to understand the specific needs and challenges of your application. Based on your feedback, we can move our project forward!
We look forward to you joining the development project!
What information can help us?
Your contact details
How is your application structured and what is the goal?
In which environment would you like to use the vision system?
Which use case are you pursuing - e.g. content recognition, process monitoring, or quality control?