Computer Vision vs. Machine Vision: A Comparison
Computer vision and machine vision are often mistakenly used synonymously. The main difference lies in their focus and scope. Although there is some overlap between the two terms, they address different challenges.
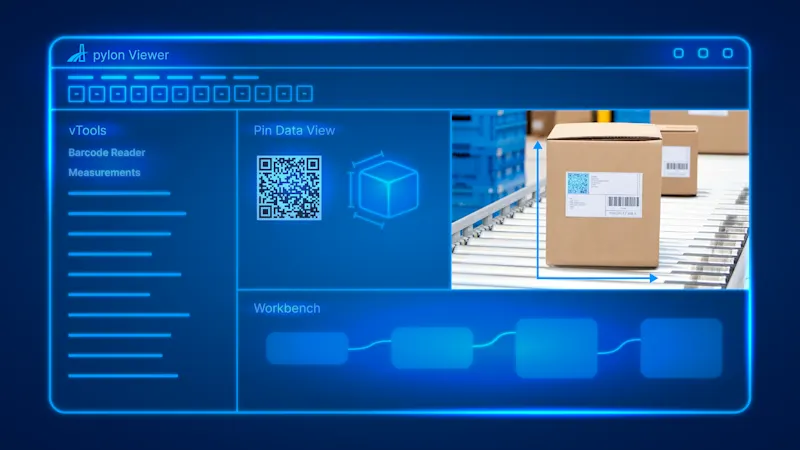
How does machine vision work?
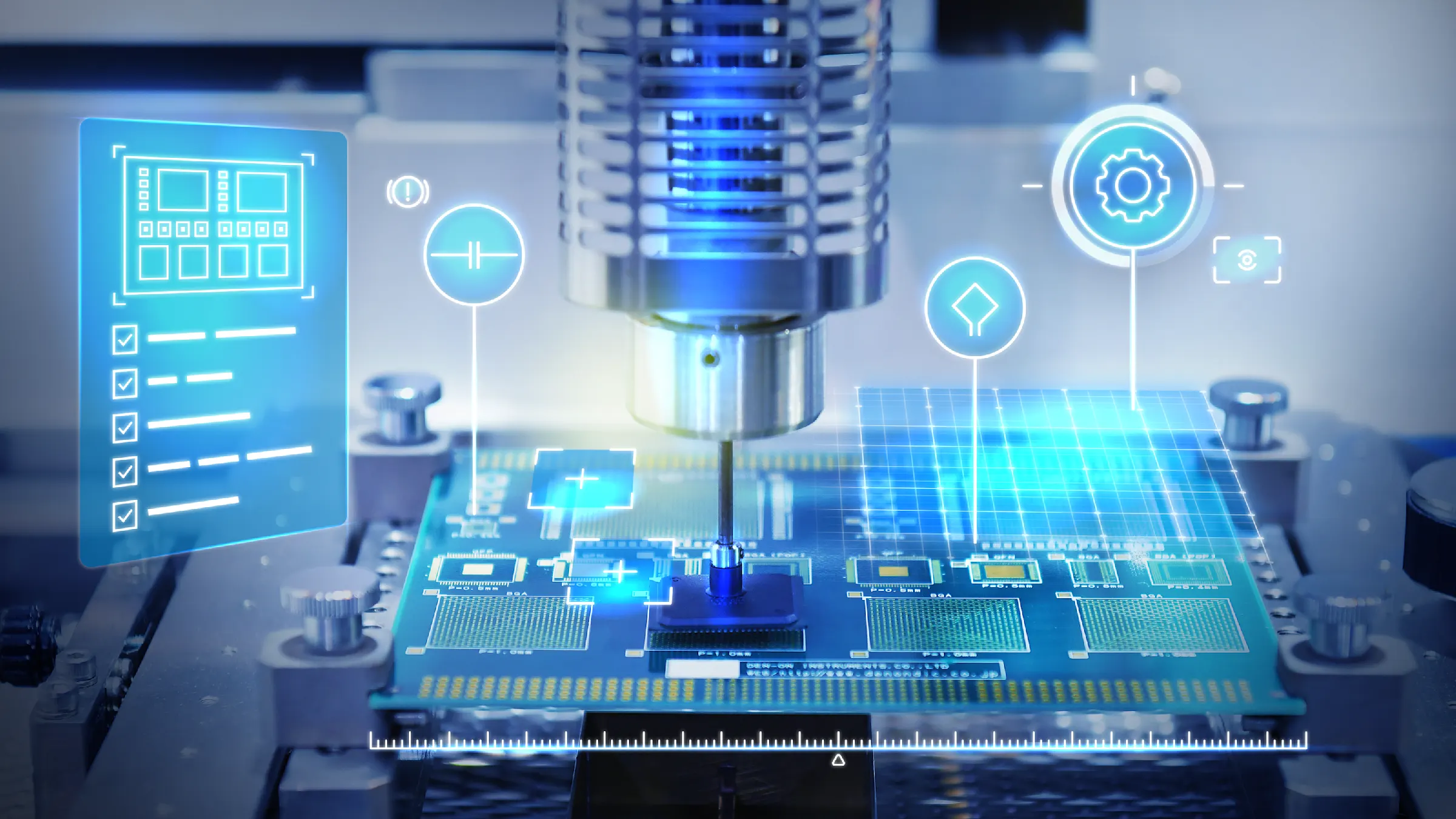
Machine vision automates repetitive, identical processes. The system uses cameras and sensors to take images of a precisely defined environment. It then processes predefined aspects of these images and uses them for various industrial applications. AI can also play a role in individual areas (e.g. optical character recognition).

Key features of machine vision
Targeted applications for specific tasks such as quality control or object recognition
Real-time processing: systems capture and analyse images in real time
Hardware integration: uses highly specialised cameras and lighting systems for optimal image capture.

Machine vision applications
Quality control: checking products for defects and faults
Component inspection: automated inspection of individual components during production
Barcode and QR code reading: automatic identification of products in logistics and retail
Robot-assisted systems: helping robots navigate and control objects
How does computer vision work?
The computer vision system is fed a wide variety of visual data, including images, photos, and videos. This data can be transmitted ‘live’ from cameras or loaded from a memory; the origin is irrelevant. These vision systems repeatedly process and analyse visual input. This enables the algorithm to learn to recognise certain patterns and objects and to gain further insights from them. The computer can then not only ‘see’ visual content, but also analyse and interpret it – in a way that is similar to how a human would.
Key features of computer vision
algorithms and AI: Computer vision uses complex algorithms and machine learning for image recognition.
Focus on interpretation: It concentrates on analysing and interpreting image data to learn more and more.

Computer vision applications
Autonomous vehicles: Detection of obstacles and road signs.
Face recognition: Use in security and surveillance systems.
Medical imaging: Analysis of X-ray images or MRI scans for diagnosis.
Agriculture: Analysis of plant growth and crop yields using image data.
Computer Vision vs. Machine Vision: Similarities and Differences
Machine vision and computer vision have some overlaps. However, they differ in their applications and focus. Computer vision systems extract a wide range of information from images, videos, and other visual representations. Machine vision systems focus on the image captured by the system's camera.
Machine Vision | Computer Vision | |
Application | Industry and manufacturing | Wide range, such as health and transport |
|---|---|---|
Targeted | Automation and inspection | Image interpretation and pattern recognition |
Real-time processing | High | Variable, often analysis-heavy |
Technology | AI | AI |
Intelligent tools with different focuses
Although machine vision and computer vision are often used synonymously, there are clear differences in their applications, objectives, and technologies. While computer vision offers a broader perspective on visual analysis and information processing, machine vision focuses on specific industrial implementations of image processing.