Embedded Vision: The Future of Intelligent Devices
Many electronic devices, such as computers or cameras, are becoming ever smaller and more powerful at the same time. This trend can also be observed in the world of image processing: Thanks to embedded vision, image processing systems can be manufactured cost-effectively and for specific applications. Find out here what exactly embedded vision means and which applications benefit from it.
Development of embedded IoT vision systems

In our webinar, you will learn how to overcome the three biggest challenges in the development of IoT systems.
Learn how to implement an optimized machine vision architecture for deploying ML models from the AWS cloud to the edge device. This enables development teams to quickly start prototyping their intelligent, networked machine vision applications.
Watch IoT webinarEmbedded vision systems - definition and functionality
Embedded vision refers to the integration of computer vision technology into intelligent devices such as cameras, smartphones, drones, and robots. This enables such devices to capture, process, and analyze visual data in real time. By integrating image processing technologies, these systems are able to perceive and interpret visual data, making them smarter and more efficient, and enabling faster decision-making and automation. Embedded vision systems consist of sensors that capture visual data, processors that analyze the data, and software that performs specific tasks based on the analysis.

How do embedded vision technologies work?
Embedded vision systems combine image processing with artificial intelligence and work by capturing visual data from the environment using sensors such as cameras. The data is then processed using specialized hardware and software to extract relevant information. The extracted information can be used for a variety of applications such as object recognition, facial recognition, gesture recognition, and augmented reality.

Structure of an embedded vision system
An embedded vision system consists of several components that capture, process, and output visual data:
Small camera: The first component is a small camera. It captures visual data and converts it into a digital signal.
Processing board: The digital signal is then forwarded to an image processor, which analyzes and processes the data and sends it to an output processor.
Cable: The camera is usually connected directly to the processing board via a short cable.
These components are integrated into a larger system. A PC in industrial image processing is suitable for general purposes, while processing boards in an embedded vision system are developed for application-specific tasks.
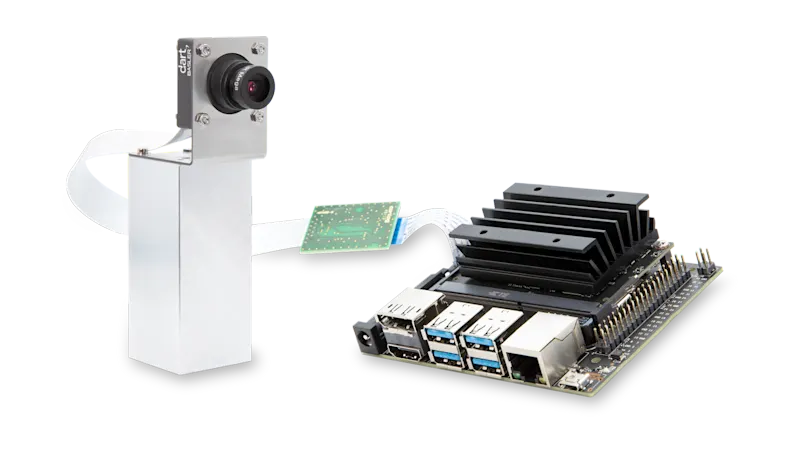
How are embedded vision cameras integrated?
For image processing applications, integration usually takes place via a GigE interface or USB interface, which is connected to a PC as a plug-and-play solution. In conjunction with a software development kit from the manufacturer, the camera can be easily accessed.
In addition to standard interfaces such as USB, flexible low-level interfaces are chosen in embedded applications as they offer advantages in direct connection scenarios. However, these interfaces require knowledge of embedded technologies - the integration effort can therefore be higher.
Five Expert Tips for Embedded Vision Systems
The embedded design opens a variety of possibilities for new computer vision applications. But the technology also has its pitfalls. Our expert Thies Moeller shows some of the most common mistakes in the design und use of embedded vision systems and explains how to avoid these.
Applications at a glance
Embedded vision systems can open up new markets, improve safety in various applications, and automate processes and make them more efficient.
Medical & Life Sciences
In healthcare, embedded vision is used for medical image processing, disease detection, patient monitoring, and diagnosis. For example, embedded vision systems can capture high-resolution images of internal organs, detect abnormalities, analyze X-ray and MRI images, and support surgical procedures. Classic examples from everyday medical practice include portable fundus cameras that can capture an image of the back of the eye or a digital dermatoscope for examining skin lesions.
Automotive industry
Integrated image processing technologies are used in the automotive industry to improve safety and efficiency. It enables advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), autonomous driving, and interior monitoring. In addition, embedded vision systems can recognize objects, pedestrians and traffic signs and provide real-time feedback to the driver.

Robotics
Embedded vision is also revolutionizing the field of robotics by enabling robots to navigate autonomously, interact with their environment and perform complex tasks. Vision-guided robotics can be used for quality control, inspection and assembly, for example.

Security
Embedded technologies are used in security systems to detect and monitor suspicious behavior. They can identify people, track their movements, and detect unauthorized access to restricted areas. These solutions can also analyze video footage and alert security personnel to suspicious activity.
Advantages of embedded vision technologies
Real-time processing: integrated image processing technologies can process and analyze large amounts of visual data in real time, enabling real-time decisions and feedback. This is crucial in applications such as autonomous driving, where decisions need to be made quickly and accurately.
Low energy consumption: Embedded vision systems are designed to be energy efficient, which is crucial for mobile devices such as smartphones and drones.
Small size: The small dimensions of embedded vision systems make it possible to integrate them into almost any application.
Cost-effective: The components of integrated image processing technologies have a low unit price, which makes them an economical option for companies.
A small solution with a big impact - a glimpse into the future
The world will see more and more embedded vision solutions in the coming years. Application-specific vision systems offer an innovative and cost-effective alternative to generic computers, as the PC comes with a lot of unnecessary hardware and software. Embedded vision systems are also very light and compact. This means that previously stationary devices can even be made mobile and portable.
Embedded vision technologies are enabling a whole new generation of products. Advances in artificial intelligence (AI) will also help embedded vision systems to become even more intelligent and effective, enabling them to take on a variety of tasks in different industries and create competitive advantages.